Treatment of Patients With Obesity
Obesity is a complex, chronic condition that affects millions of people worldwide. Characterized by excessive body fat, it poses significant health risks, including heart disease, diabetes, and certain cancers. Treating obesity requires a multifaceted approach that addresses the root causes and helps patients achieve sustainable, long-term weight loss.
1. Understanding Obesity: Beyond Diet and Exercise
- Complex Causes: Obesity is not simply a result of overeating or lack of exercise. It is influenced by a range of factors, including genetics, metabolism, environment, and behavior. Some individuals may be more predisposed to gaining weight due to their genetic makeup, while others may be affected by hormonal imbalances or psychological factors such as stress and depression.
- Health Implications: Obesity increases the risk of numerous health conditions, including type 2 diabetes, hypertension, heart disease, stroke, sleep apnea, and certain types of cancer. It also has a significant impact on mental health, often leading to low self-esteem, anxiety, and depression.
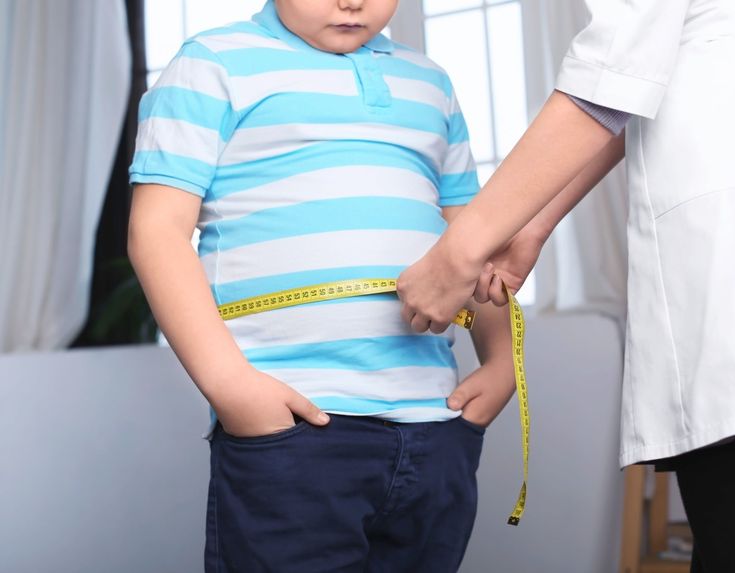

2. Behavioral Modifications: The Foundation of Treatment
- Dietary Changes: One of the first steps in treating obesity is adopting a healthier diet. This involves reducing caloric intake, choosing nutrient-dense foods, and avoiding processed foods high in sugars and unhealthy fats. A balanced diet that includes plenty of fruits, vegetables, lean proteins, and whole grains is essential for weight loss and overall health.
- Physical Activity: Regular physical activity is crucial for managing obesity. Exercise helps burn calories, build muscle, and improve cardiovascular health. Patients are encouraged to engage in activities they enjoy, such as walking, swimming, or cycling, to increase the likelihood of long-term adherence. Starting with small, manageable goals and gradually increasing intensity and duration can help patients incorporate exercise into their daily routine.
- Behavioral Therapy: Behavioral therapy can help patients identify and change unhealthy eating patterns, cope with emotional eating, and develop strategies for maintaining weight loss. Cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT) is particularly effective in addressing the psychological aspects of obesity, helping patients understand the connection between their thoughts, emotions, and behaviors related to food and exercise.
3. Medical Interventions: When Lifestyle Changes Aren’t Enough
- Pharmacotherapy: For some patients, lifestyle changes alone may not be sufficient to achieve significant weight loss. In such cases, medications may be prescribed to help reduce appetite, increase feelings of fullness, or decrease the absorption of fat. These medications are typically used in conjunction with diet and exercise and are most effective when combined with behavioral modifications.
- Bariatric Surgery: In cases of severe obesity or when other treatments have failed, bariatric surgery may be considered. Procedures such as gastric bypass, sleeve gastrectomy, and adjustable gastric banding reduce the size of the stomach or alter the digestive process, leading to significant weight loss. Bariatric surgery is often life-changing for patients with obesity, but it requires a lifelong commitment to dietary changes and regular medical follow-ups to ensure long-term success.
4. Addressing Underlying Psychological Factors
- Mental Health Support: Obesity is often accompanied by psychological challenges, including depression, anxiety, and body image issues. Addressing these underlying factors is crucial for successful treatment. Counseling, support groups, and stress management techniques can help patients build a healthier relationship with food and their bodies.
- Motivation and Goal Setting: Maintaining motivation is one of the biggest challenges in treating obesity. Setting realistic, achievable goals can help patients stay focused and committed to their treatment plan. Celebrating small victories and recognizing progress, even when it’s slow, can boost morale and reinforce positive behavior changes.
5. Long-Term Management and Prevention of Relapse
- Sustainable Habits: Long-term success in treating obesity requires the development of sustainable, healthy habits. Quick fixes and fad diets may lead to temporary weight loss, but they are often followed by a return to previous eating habits and weight regain. Emphasizing gradual, permanent changes in diet and lifestyle is key to maintaining weight loss over time.
- Ongoing Support: Continuous support from healthcare providers, family, and friends is crucial for long-term weight management. Regular follow-up appointments with a healthcare provider can help monitor progress, address any challenges, and make necessary adjustments to the treatment plan. Support groups and counseling can also provide ongoing encouragement and accountability.
6. The Role of Healthcare Providers
- Comprehensive Care: Treating obesity requires a team approach that includes primary care physicians, dietitians, psychologists, and exercise specialists. This multidisciplinary team works together to create a personalized treatment plan that addresses the unique needs and challenges of each patient.
- Patient-Centered Approach: Healthcare providers should adopt a patient-centered approach, focusing on the individual’s goals, preferences, and readiness to change. It’s important to address any barriers to treatment, such as lack of access to healthy foods, time constraints, or financial limitations, and to provide the necessary support and resources to overcome these challenges.
Conclusion: A Lifelong Journey
Treating obesity is not a one-size-fits-all process. It requires a comprehensive, individualized approach that addresses the physical, psychological, and social aspects of the condition. Success in treating obesity involves not just weight loss, but also improving overall health and quality of life.
Healthcare providers play a vital role in supporting patients on their journey to better health, offering guidance, encouragement, and evidence-based treatments that lead to lasting change. By focusing on long-term management and prevention of relapse, patients with obesity can achieve and maintain a healthier weight, reducing their risk of chronic diseases and enhancing their overall well-being.